September 2024
North America News
加拿大已针对某些全氟和多氟烷基物质(PFAS)发布了特定通知。根据《加拿大1999环境保护法》第71(1)(b)条款(简称“法案”),为了评估所描述物质的毒性或控制方法,相关人员须在2025年1月29日之前提供特定信息。
主要内容如下:
1. 谁需要回应?
此通知适用于2023日历年度期间的任何人,
生产总量超过1 000克的任何在附表1中列出的物质。
进口总量超过10克列于附表1第一部分的物质,或附表1第二部分或第三部分的物质总量超过100千克。
进口附表1中列出的任何物质在制造物品中浓度≥1 ppm,总量超过100千克但未列入制造物品类别。
使用总量超过10克的任何在附表1中列出的物质,无论该物质是单独存在的还是在混合物或产品中的浓度≥1 ppm,在制造混合物、产品或制造制品时使用。
2. 如何确定您是否符合报告标准(通知第2部分)
分级报告(注意第3节)
如果您的制造项目符合其中一个类别且超过阈值,您必须提供通知中请求的所有信息。
如果您的制造物品不属于任何类别并且超过了阈值要求,您只需要根据通知第8部分提供公司信息,并根据通知第9部分提供含有该物质的制造物品的简短描述和通用名称。
继任者或受让人(通知第4部分)
如果一家公司在2023日历年度期间被出售,可以提交一个综合了转让前后信息的全年响应。
排除项(通知第5和6部分)
该通知不适用于:
员工少于5人的小型企业或年总收入少于30,000美元的小型企业
该通知还不适用于以下物质、混合物、产品和制造物品:
仅在加拿大过境或个人用途
用于实验室分析或科学研究
分类为危险废物或危险可回收材料,且进口/出口符合跨境危险废物和危险可回收材料运输法规。
根据《有害生物防治产品法》,《肥料法》,《饲料法》或《种子法》注册。
3. 需要哪些信息(注意第7至第14节)
1. 如果您确定自己符合通知的报告条件,必须提供包含必要信息的响应,摘要如下:
识别信息(公司/组织和报告人)
设施信息
生产、进口、用于制造商品和出口的物质数量
商品信息
2. 关于完成对通知第8-14部分的响应的详细解释、示例和提示,请参见 附件A。
3. 请注意,如果您拥有多个设施,您必须在公司范围内考虑报告标准。您对通知的响应必须整合公司所有设施的信息(注意第7节)。
所需的附加信息:合理可获取的信息;保密商业信息。
4.如何响应通知
确定是否符合报告标准后,有三种方式响应通知:
CEPA第71部分响应
如果您符合报告标准,您必须通过提交所需信息以Excel报告文件(ERF)的形式响应通知,并提交给加拿大政府。
从PFAS通知响应网页下载PFAS ERF。
完成所需信息(说明请见附录A)
通过加拿大环境与气候变化单一窗口提交ERF(说明请见附录B)
利益相关者声明(SHI)
如果您不符合报告要求,但对可报告物质感兴趣,可以提交SHI。
以下是可能超出通知中列出的PFAS的部分清单:
OECD全球PFAS综合数据库(Fluorinated Chemical (oecd.org)),
美国环境保护署PFAS结构(化学品仪表板(epa.gov)),以及美国环境保护署PRAS开发(化学品仪表板(epa.gov))(说明包含在附录B中)。
不参与声明(DNE)
如果您不符合报告要求且对任何物质不感兴趣,我们建议您通过发送电子邮件至substances@ec.gc.ca提交DNE。在电子邮件主题行中注明“PFAS DNE”并注明您的公司名称和联系信息。
注意:相关人员必须在2025年1月29日之前提供特定信息。如指导手册中所述,未能响应可能会导致环境执法行动以及对个人和公司的潜在处罚。
在美国,当发现消费品存在危害时,它们将被召回并在消费者产品安全委员会(CPSC)网站上发布,该网站每天更新。2024年8月1日至2024年8月31日的美国召回情况如下所述:
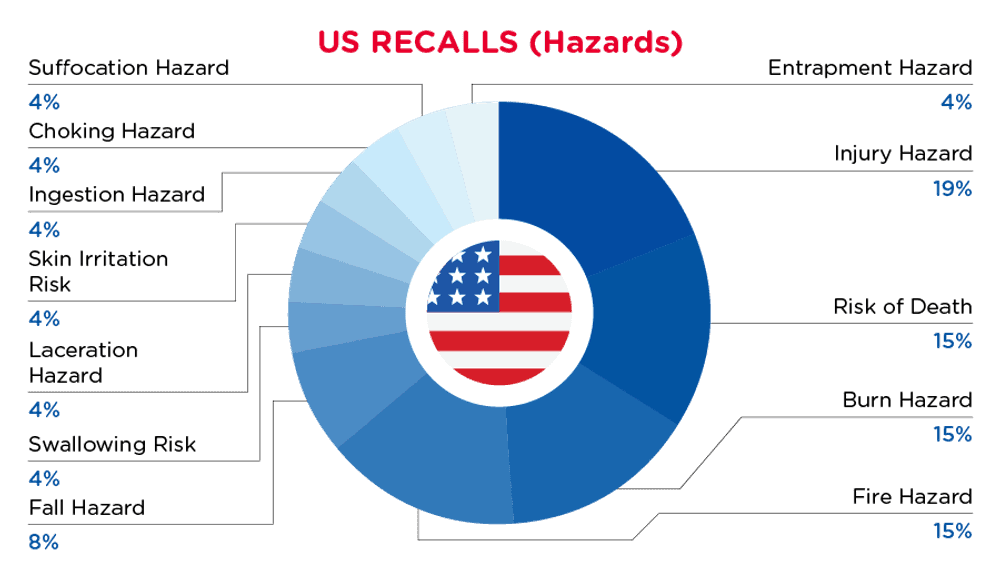
| 危险 | 频率 |
| 伤害危险 | 4 |
| 死亡风险 | 3 |
| 烧伤危险 | 3 |
| 火灾危险 | 3 |
| 坠落危险 | 2 |
| 吞咽风险 | 1 |
| 撕裂危险 | 1 |
| 皮肤刺激风险 | 1 |
| 摄入危险 | 1 |
| 窒息危险 | 1 |
| 窒息危险 | 1 |
| 诱捕危险 | 1 |

| 产品类别 | 频率 |
| 玩具和儿童护理产品 | 8 |
| 电器 | 3 |
| 家用电器 | 3 |
| 家居用品 | 2 |
| 体育用品/装备 | 2 |
| 化学品 | 1 |
| 织物 / 纺织品 / 服装 / 家纺 | 1 |
| 机械 | 1 |
| 户外生活用品 | 1 |
要获取完整列表,请单击此处
在加拿大,当消费品存在危险时,它们将被召回并公布在卫生加拿大网站的召回和安全警报数据库中,该数据库每天更新。加拿大从2024年8月1日至2024年8月31日期间的召回情况如下:
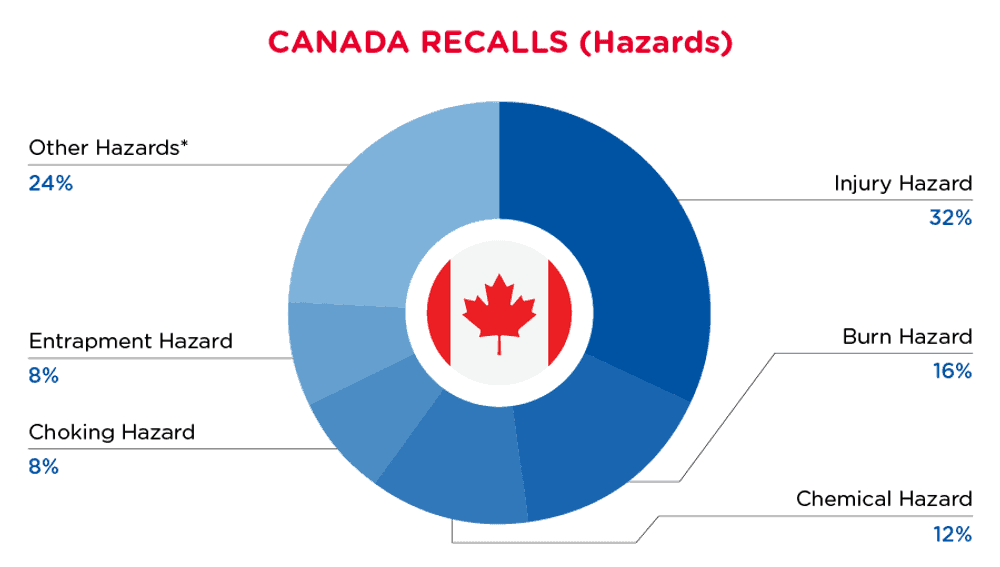
| 危险 | 频率 |
| 伤害危险 | 8 |
| 烧伤危险 | 4 |
| 化学危害 | 3 |
| 窒息危险 | 2 |
| 诱捕危险 | 2 |
| 其他危害* | 6 |
*其他危险包括对视力的损害,对皮肤的损害,火灾危险,割伤危险,死亡风险和窒息危险,频率低于2。

| 产品类别 | 频率 |
| 玩具和儿童护理产品 | 6 |
| 织物 / 纺织品 / 服装 / 家纺 | 4 |
| 身体护理/化妆品 | 2 |
| 汽车配件 | 2 |
| 化学品 | 2 |
| 电器 | 1 |
| 防护设备 | 1 |
| 家用电器 | 1 |
| 机械 | 1 |
要获取完整列表,请单击此处
Europe News
The European Commission has added a new entry of 79 in Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 which restricts the use of PFHxA, its salts and PFHxA-related substances. These sub-groups of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances will be banned in consumer textiles, food packaging, cosmetics, etc. Manufacturers with related products shall pay attention to ensure product compliance.
On 19 September 2024, the European Commission released the restriction related to the use of Perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA), its salts and PFHxA-related substances, as an important step forward in reducing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) emissions. PFHxA is often used as a substitution for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), another already banned PFAS. This was added as entry 79 in Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 which focuses on ensuring protection of human health and the environment by promoting responsible use of chemicals, encouraging the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives, and increasing transparency about the properties and uses of chemicals.
It will take effect after transitional periods of between 18 months and 5 years, depending on the use, allowing time for replacement by safer alternatives. Manufacturers with related products shall pay attention to ensure product compliance.
Having a linear or branched perfluoro pentyl group with the formula C5F11- directly attached to another carbon atom as one of the structural elements; or
Having a linear or branched perfluorohexyl group with the formula C6F13-.
The following substances are excluded from this designation:
C6F14.
C6F13-C(=O)OH, C6F13-C(=O)O-X′ or C6F13-CF2-X′ (where X′ = any group, including salts)
Any substance having a perfluoroalkyl group C6F13- directly attached to an oxygen atom at one of the non-terminal carbon atoms.
1. Reference for PFHxA-related substances
PFHxA-related substances are substances that, based on their molecular structure, are considered to have the potential to degrade or be transformed to PFHxA. A non-exhaustive list of substances belonging to the scope of the restriction proposal is available on the website of the European Chemicals Agency.
2. Phase-Out Schedule
| Regulation | Product/Scope | Requirement | Effective Date |
| EU REACH Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 Annex XVII Entry 79 | - Textiles, leather, furs and hides in clothing and related accessories for the general public. - Footwear for the general public. - Paper and cardboard used as food contact materials. - Cosmetics. - Mixtures for the general public. | PFHxA and its salts: ≤ 25 ppb PFHxA related substances ≤ 1000 ppb | 10 October 2026 |
| Textiles, leather, furs and hides, other than in clothing and related accessories referred to 1), for the general public. | 10 October 2027 | ||
| Firefighting foams/ concentrates for training and for testing, or for public fire services, except where those services intervene at industrial fires at establishments covered by Directive 2012/18/EU (relating to the control of major-accident hazards involving dangerous substances) | 10 April 2026 | ||
| Firefighting foams/ concentrates for civil aviation (including in civilian airports) | 10 October 2029 |
The restriction shall not apply to the following:
Personal protective equipment within the scope of Regulation (EU) 2016/425 (outlines requirements for the design, manufacture, and marketing of personal protective equipment (PPE)).
Medical devices within the scope of Regulation (EU) 2017/745 (medical device specific regulation).
In Vitro diagnostic medical devices within the scope of Regulation (EU) 2017/746 (sets standards for in vitro diagnostic medical devices).
Substances having a perfluoroalkyl group C6F13- directly attached to a sulphur atom that are prohibited in Annex I to Regulation (EU) 2019/1021 (POP) (protects human health and the environment by restricting or banning the production and use of persistent organic pollutants (POPs)).
It will be important for manufacturers to focus on the effective dates for their representative products to ensure compliance.
The European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare recently updated the technical guide for food contact metals and alloys to 2024 2nd -edition. This guide can be applied immediately.
On 1 August 2024, the European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare (EDQM), updated the technical guide for food contact metals and alloys. Compared with the previous 1st edition, the revised 2nd edition represents a significant update. The main changes are as follows:
1. Scope revised:
Removed the description of “metals and alloys used in food contact materials and articles that are covered by an organic surface coating that has been demonstrated to restrict release of metal ions to less than the applicable specific release limit” from the unapplicable scope.
That means all coated metal and alloy should follow the requirements in this guide.
Specific release limit (SRL) updated:
Table 1- SRLs for metals and alloy components
| Item | Element | SRL in 2nd guide (mg/kg food) | SRL in 1st guide (mg/kg food) |
| 1 | Aluminum (Al) | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | Antimony (Sb) | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 3 | Chromium (Cr) | --- | 0.250 |
| 4 | Chromium (Cr) (III) | 1 | --- |
| 5 | Cobalt (Co) | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| 6 | Copper (Cu) | 4 | 4 |
| 7 | Iron (Fe) | 40 | 40 |
| 8 | Magnesium (Mg) | ---b | --- |
| 9 | Manganese (Mn) | 0.55 | 1.8 |
| 10 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| 11 | Nickel (Ni) | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| 12 | Silver (Ag) | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| 13 | Tin (Sn) | 100a | 100 |
| 14 | Titanium (Ti) | ---b | --- |
| 15 | Vanadium (V) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 16 | Zinc (Zn) | 5 | 5 |
| 17 | Zirconium (Zr) | 2 | --- |
a Except in the field of application under Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/915 on maximum levels for certain contaminants in food.
b The generic SRL of 60 mg/kg food is not applicable.
Table 2- SRLs for metals as contaminants and impurities
| Item | Element | SRL in 2nd guide (mg/kg food) | SRL in 1st guide (mg/kg food) |
| 1 | Arsenic (As) | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 2 | Barium (Ba) | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| 3 | Beryllium (Be) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 4 | Cadmium (Cd) | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| 5 | Lead (Pb) | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| 6 | Lithium (Li) | 0.048 | 0.048 |
| 7 | Mercury (Hg) | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| 8 | Thallium (Tl) | 0.001 | 0.0001 |
3. Updated declaration of compliance (DoC):
The 2024 2nd edition removed the previous Chapter 4 of DoC part.
The DoC of products regulated in this guide should follow the requirements in Section 8.2 of Resolution CM/Res (2020)9 on the safety and quality of materials and articles for contact with food.
4. Optimized test conditions:
Added instruction for material/article in contact with dry food:
If an article is intended for contact with only a specific dry food, it should be tested with that food.
Updated test conditions for different types of migration:
Removed specific test conditions for fillable and non-fillable articles; follow actual conditions of use or apply the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC) Guide on testing conditions for kitchenware articles.
Changed the test method for hot beverage appliances:
Replaces DIN 10531 with EN 16889:2016.
Applied a reduction factor of 5 to the SR of silver for silver or silver-plated cutlery in the following products:
Type of class FSI/CAH1* in JRC guide, testing with citric acid as a simulant.
Articles regulated by EN ISO 8442-2, Materials and articles in contact with foodstuffs — Cutlery and table holloware.
Articles labeled not for daily use or not suitable for cooking and food preparation.
This revised technical guide can be used for immediate reference.
In June 2024, the European Committee proposed the draft regulation to update the limitation of use of BPA, as well as to introduce the harmonized classification of bisphenols and bisphenol derivatives potentially used in food contact materials. This regulation is intended to go into effect in November 2024.
The European Union (EU) drafted a regulation addressing updates particular to Bisphenol A (BPA) and other bisphenols and bisphenol derivatives in certain food contact materials (FCM) and articles in June 2024. This draft regulation is a specific measure within the meaning of Article 5 of Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004, relating to materials and articles intended to come into contact with foodstuffs.
The main points in the draft EU regulation are:
1. Definitions:
Table 1
| bisphenol | a substance consisting of two hydroxyphenyl functional groups linked by one bridging atom, in accordance with structure A: - Including the salt form of a bisphenol. - Additional groups may be attached to the bridging atom (structure A) |
| bisphenol derivative | A substance indicated by the following structure B: - Not including the salt form of a bisphenol. - R1 to R10 refers to any substituent. At least one of the substituents is not a hydrogen atom (H), e.g., BADGE (CAS 1675-54-3) - X refers to any bridging group separating the two phenyl rings by one single atom, but the atom can have any substituent(s). (structure B) |
| Hazardous bisphenol or hazardous bisphenol derivative | A bisphenol or a bisphenol derivative listed in Part 3 of Annex VI to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, due to its harmonized classification as category 1A or 1B ‘mutagenic’, ‘carcinogenic’, ‘toxic to reproduction’ or category 1 ‘endocrine disrupting’ for human health’ |
2. Current application of BPA
3. Prohibition of BPA:
Table 2
| Item | Draft BPA regulation | EU 10/2011 |
| Tolerable Daily Intake (TDI) | TDI in 2023: 0.2 ng/kg | TDI in 2015: 4 μg/kg |
| Requirement | BPA and its salts prohibited Specific migration limits (SML) for the derogation: ND (DL: 1μg/kg) | 0.05 mg/kg |
| Restrictions and Specifications | By way of derogation from BPA prohibition, BPA and its salts may be used in the manufacture of: epoxy resins to be applied on self-supporting food contact materials or articles with a capacity greater than 1000 liters. a monomer or starting substance in the manufacture of polysulfone filtration membrane assemblies. | Not to be used for the manufacture of polycarbonate infant feeding bottles. Not to be used for the manufacture of polycarbonate drinking cups or bottles which, due to their spill proof characteristics, are intended for infants and young children. |
4. Restriction of other bisphenols and bisphenol derivatives:
FCM manufactured using another bisphenol or bisphenol derivative shall not contain any residual BPA.
Without evaluation and authorization, hazardous bisphenols other than BPA or hazardous bisphenol derivatives are prohibited.
5. Verification of compliance:
BPA residual: extraction method.
BPA migration: the rules and parameters are the same as EU 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food.
Analytical methods uniformly applied throughout the Union are required to be developed.
6. Declaration of compliance:
Accompany the FCM at all stages of placing on the market, except during the retail stage.
Include an indication whether BPA or other relevant bisphenols or bisphenol derivatives have been used.
7. Transition period:
Table 3
| Product types | Transition period |
| General articles | 18 months |
| Packaging with varnishes and coatings manufactured with BPA, specifically used to preserve fruit, vegetables and processed fish products | 36 months |
| Metal packaging in which external/ internal surfaces have had BPA varnishes and coatings applied | 36 months |
| Single-use final FCM (including metal packaging) | Should be filled with food and sealed within 12 months from the end of the respective transitional periods, until exhaustion of stocks. |
| Repeat-use components in professional food production equipment, such as confectionary molds, seals, pumps, flanges, gauges and sight glasses | 36 months |
| Repeat-use final food contact articles that have been first placed on the market by their manufacturers | In order to avoid large stocks, sales can continue for a maximum period of one year. |
| Repeat-use final food contact articles used as professional food production equipment | Continue to use until falling into disuse. |
8. Relationship with other regulations:
1. Repeal Regulation (EU) 2018/213 on the use of bisphenol A in varnishes and coatings intended to come into contact with food
The measures provided for in this Regulation supersede the measures laid down in Regulation (EU) 2018/213. It is therefore appropriate to repeal (EU) 2018/213.
2. Amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011
By way of derogation from Article 5, BPA and other hazardous bisphenols or hazardous bisphenol derivatives added.
In Table 1 of Annex I, the entries concerning substance No. 151 (BPA) and substance No. 154 (BPS) are deleted.
This draft regulation is intended to go into effect in November 2024.
欧洲化学品管理局已宣布就将六种化学品列为高关注物质(SVHC)启动谘询阶段。 如果这些清单获批准,候选名单中被认可为SVHC的物质数量将更新至247项。
2024年8月30日,欧洲化学品管理局 (ECHA) 启动了一个为期45天的公开咨询,关于新增的六种潜在高关注物质 (SVHC),详见下表。
如果得到批准,候选名单中的SVHC数量将从241项更新至247项。
在45天咨询期结束后,将决定是否将以下物质列入ECHA的高关注物质候选名单中。
| 物质名称 | 欧洲委员会编号 | 化学文摘社编号 | 提议理由 |
| 6-[(C10-C13)-烷基-(分支、不饱和)-2,5-二氧基吡咯烷-1-基]己酸 | 701-118-1 | 2156592-54-8 | 对生殖有毒 (第 57c 条) |
| O,O,O-三苯基硫代磷酸酯 | 209-909-9 | 597-82-0 | PBT (第57条第d款) |
| 八甲基三硅氧烷 | 203-497-4 | 107-51-7 | vPvB (第57条第e款) |
| 全氟胺 | 206-420-2 | 338-83-0 | vPvB (第57条第e款) |
| 反应物:三苯基硫代磷酸酯和叔丁基苯衍生物 | 421-820-9 | 192268-65-8 | PBT (第57条第d款) |
| 三(4-壬基苯基, 支链和线性)磷酸酯 | / | / | 内分泌干扰特性 (第57条第f款 – 环境) |
The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) recently updated recommendations for five types of food contact materials. A manufacturer of silicone/paper/ temperature-resistant coatings should be aware that test methods or requirements has been revised. These updated documents can be applied immediately.
On 1 August 2024, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) issued five updated recommendations relative to food contact materials. Following are the updated recommendations and affected food contact materials:
| Reference # | |
| XV | Silicones |
| XXXVI | Paper and Board for Food Contact |
| XXXVI/1 | Cooking Papers, Hot Filter Papers and Filter Layers |
| XXXVI/2 | Paper and Paperboard for Baking Purposes |
| LI | Temperature Resistant Polymer Coating Systems for Frying, Cooking and Baking Utensils |
The main changes of the requirements and test methods are:
1. For XV Silicones:
Deleted the requirement for extractable components (Section III, 5) not exceeding 0.5%.
Updated the test method for Volatile Organic Matter (VOM):
Table 1
| Item | Updated version on 1 August 2024 | Previous version |
| VOM | After conditioning, specimen is tested at 200℃ for 4 hours. | After conditioning, specimen is tested at 200℃ for 4 hours. |
| VOM | Articles that cannot withstand above testing conditions, can apply alternative conditions in Table 3 of Annex V in Regulation (EU) 10/2011. | After conditioning, specimen is tested at 200℃ for 4 hours. |
2. For XXXVI Paper and Board for Food Contact:
Updated the requirement for Phthalates for recycled paper:
Table 2
| Specified Phthalate | Updated version on 1 August 2024 | Previous version |
| DEHP | 0.6 mg/kg | 1.5 mg/kg |
| DBP | 0.12 mg/kg | 0.3 mg/kg |
| DIBP | 0.15 mg/kg | 0.3mg/kg |
| Sum of (DBPx5 + DIBPx4 + DEHPx1) report as DEHP | 0.6mg/kg | / |
3. For XXXVI/1 Cooking Papers, Hot Filter Papers and Filter Layers and XXXVI/2 Paper and Paperboard for Baking Purposes:
There is no update for requirement or test method.
Compared with previous version, species of additives have been included.
4. For LI Temperature Resistant Polymer Coating Systems for Frying, Cooking and Baking Utensils:
Added requirement of 10mg/dm2 for overall migration of 3rd migration test. Test conditions as follows:
95% ethanol, 60 ℃ for 6 hours.
Isooctane, 60 ℃ for 4 hours.
Updated test conditions for specific migration:
Remove test conditions in previous version.
Apply test conditions in European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC) Guide for food preparation utensils under classes FPU/H2, FPU/H3, and a modified time for FPU/H4 to 4 hours.
Apply modified polyphenylene oxide (MPPO) as simulant for article contact with dry food; test condition is 175 °C for 2 hours (DIN EN 14338).
Apply the current version of European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EQDM) Technical Guideline for Metals and Alloys for element migration testing.
Note: These updated documents can be applied immediately.
在欧洲,当非食品消费品中发现危害时,产品将被召回并在安全门系统中公布。该系统每周更新一次。2024 年 8 月 1 日至 2024 年 8 月 31 日的欧洲召回情况总结如下:
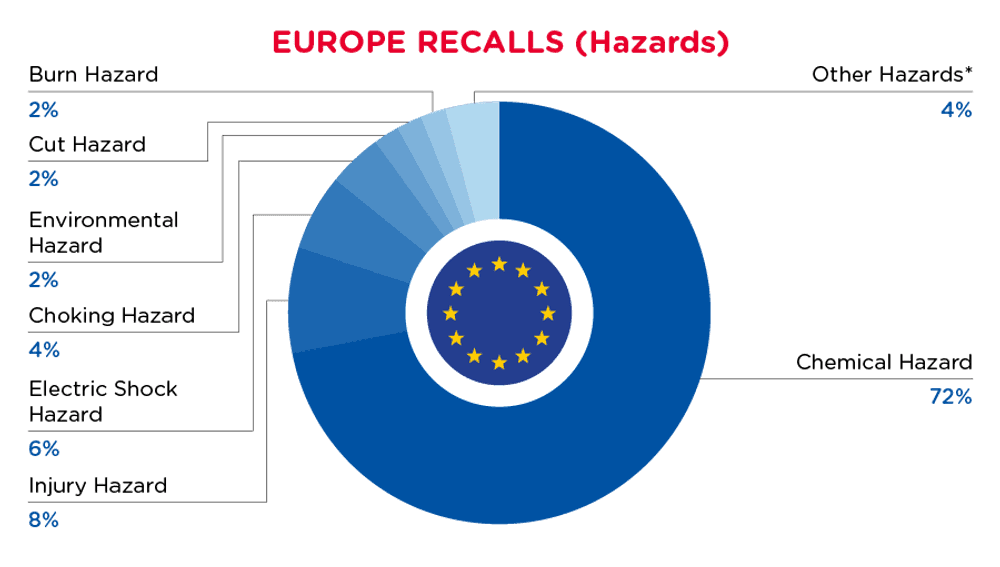
| 危险 | 频率 |
| 化学危害 | 398 |
| 伤害危险 | 42 |
| 电击危险 | 31 |
| 窒息危险 | 21 |
| 环境危害 | 13 |
| 切割危险 | 12 |
| 烧伤危险 | 12 |
| 其他危害* | 24 |
*其他危险包括勒死危害、视力损伤、溺水危害、火灾危害、窒息危害、听力损伤、微生物危害和夹困危害,发生频率低于 7 次。

| 产品类别 | 频率 |
| 身体护理/化妆品 | 336 |
| 玩具和儿童护理产品 | 50 |
| 电器 | 34 |
| 化学品 | 33 |
| 机械 | 22 |
| 织物 / 纺织品 / 服装 / 家纺 | 13 |
| 其他类别* | 35 |
*其他类别包括家用电器、户外生活用品、防护设备、运动用品/设备、珠宝、计算机/音频/视频/其他电子产品及配件、食品接触材料、工具和五金、家具和鞋类,发生频率低于 8 次。

| 通知国家 | 频率 |
| 意大利 | 294 |
| 匈牙利 | 55 |
| 捷克 | 38 |
| 丹麦 | 20 |
| 瑞典 | 15 |
| 法国 | 14 |
| 芬兰 | 14 |
| 立陶宛 | 13 |
| 波兰 | 13 |
| 奥地利 | 10 |
| 其他国家* | 37 |
*其他国家包括德国、斯洛伐克、罗马尼亚、塞浦路斯、挪威、爱尔兰、荷兰、保加利亚、比利时和拉脱维亚,发生频率低于 10 次。
欲获得完整列表请点击此处
China News
在中国,当消费品中发现危害时,它们将被召回并在国家市场监督管理总局不合格产品管理中心发布,该网站每天更新。中国从2024年8月1日至2024年8月31日的召回情况如下:
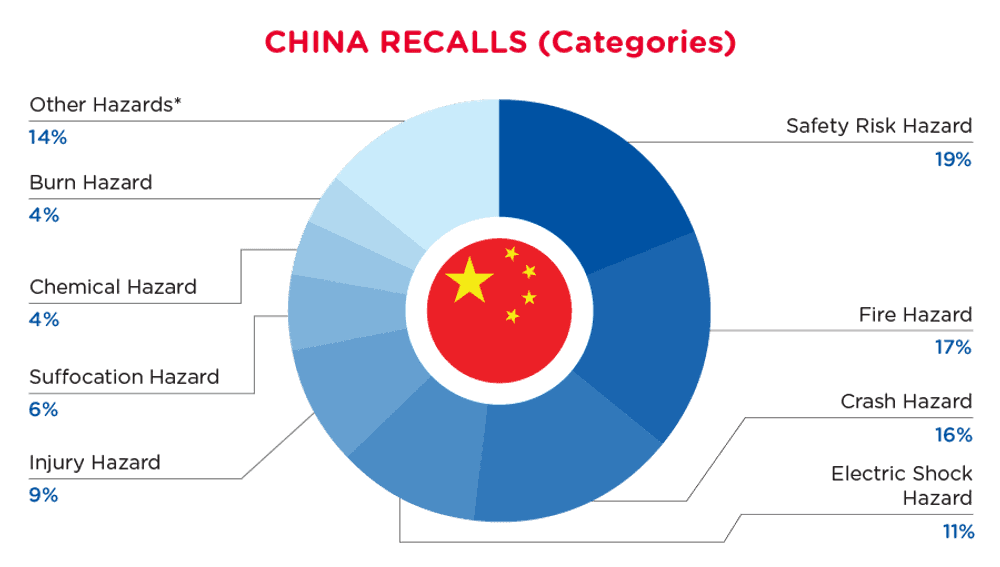
| 危险 | 频率 |
| 安全风险 危险 | 25 |
| 火灾危险 | 23 |
| 碰撞危险 | 21 |
| 电击危险 | 15 |
| 伤害危险 | 12 |
| 窒息危险 | 8 |
| 化学危害 | 6 |
| 烧伤危险 | 5 |
| 其他危害* | 19 |
*其他危害包括爆炸危险、误食风险、摔倒危险、损害视力、损害听力、刺穿危险、缠绕危险、健康风险和切割危险,频率低于4次。

| 产品类别 | 频率 |
| 体育用品/装备 | 44 |
| 玩具和儿童护理产品 | 21 |
| 家用电器 | 6 |
| 电器 | 5 |
| 文具 | 3 |
| 其他类别* | 7 |
*其他类别包括食品接触材料、计算机/音频/视频/其他电子产品及配件、家居用品、面料/纺织品/服装/家用纺织品、个人防护设备和工具及五金,频率少于3次。
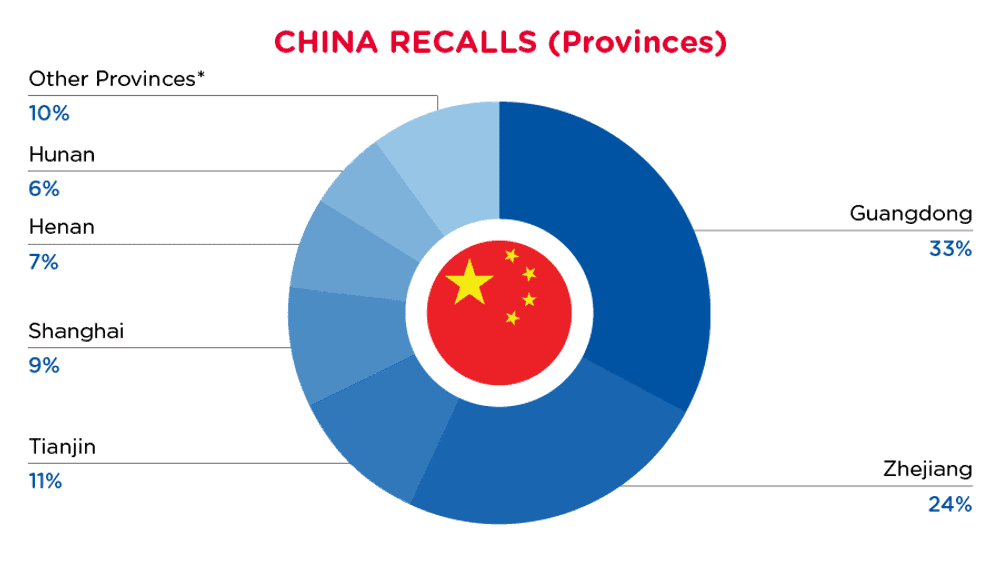
| 省份 | 频率 |
| 广东 | 28 |
| 浙江省 | 21 |
| 天津 | 9 |
| 上海 | 8 |
| 河南 | 6 |
| 湖南 | 5 |
| 其他省份* | 9 |
*其他省份包括内蒙古、福建、江苏、四川、辽宁和山西,频率低于2次。
点击此处查看完整列表
Australia/New Zealand News
在澳大利亚,当发现消费品存在危害时,它们将被召回并在澳大利亚竞争与消费者委员会网站的“召回和安全警报数据库”中发布,该网站每天更新。澳大利亚从2024年8月1日至2024年8月31日的召回情况如下所述:
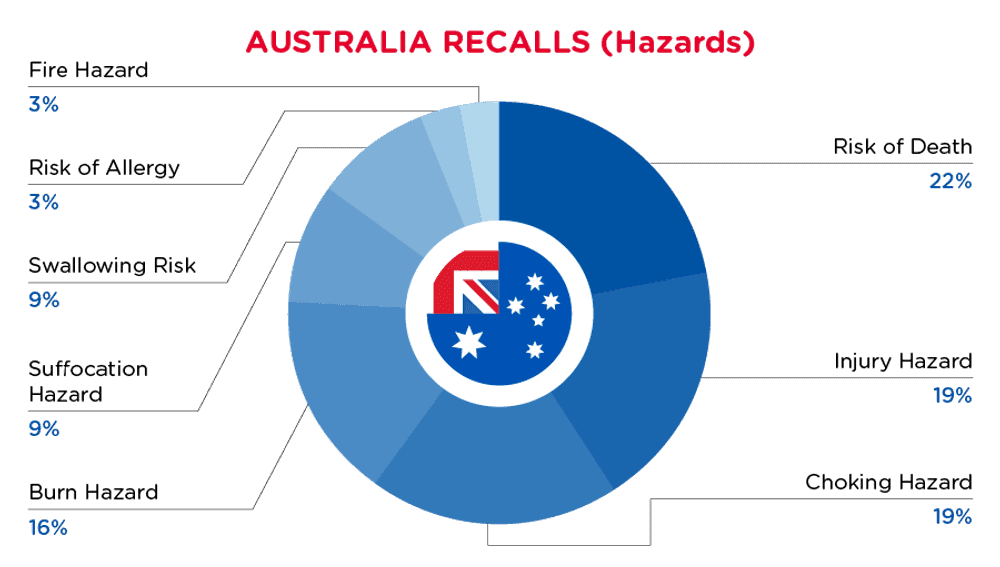
| 危险 | 频率 |
| 死亡风险 | 7 |
| 伤害危险 | 6 |
| 窒息危险 | 6 |
| 烧伤危险 | 5 |
| 窒息危险 | 3 |
| 吞咽风险 | 3 |
| 过敏风险 | 1 |
| 火灾危险 | 1 |

| 产品类别 | 频率 |
| 织物 / 纺织品 / 服装 / 家纺 | 5 |
| 玩具和儿童护理产品 | 2 |
| 电器 | 2 |
| 体育用品/装备 | 2 |
| 身体护理/化妆品 | 1 |
| 家居用品 | 1 |
要查看完整列表,请单击此处
USA Federal News
2024 年 9 月 5 日,美国 环境保护署(EPA) 发布了一项 直接最终规则,将 PFAS 数据提交期的开始时间推迟到 2025 年 7 月 11 日。现行规则下的报告和记录保存要求(40 CFR 第 705 部分)没有其他变化。
美国环境保护署(EPA)于 2024 年 9 月 5 日发布了一项直接最终规则,将有毒物质控制法(TSCA)下对全氟和多氟烷基物质(PFAS)数据报告和记录保存的要求的数据提交开始日期从 2024 年 11 月 12 日推迟到 2025 年 7 月 11 日。现行规则下的报告和记录保存要求(40 CFR 第 705 部分)没有其他变化。
关于 TSCA 第 8(a)(7) 条对 PFAS 报告和记录保存要求的背景
根据 2023 年 10 月发布的法规,2011 年至 2022 年间任何一年内生产(包括进口) PFAS 的制造商必须向 EPA 报告某些与暴露、环境和健康影响相关的数据。
由于一般预算问题和资源限制,EPA 的承包商减少了对 TSCA 信息技术软件和相关组合的努力超过 50%,这对 EPA 在许多信息技术/信息管理 (IT/IM) 项目上的进展产生了重大且立即的影响。
为了确保报告功能正常,EPA必须延长开发项目的时间表。因此,数据提交期的开始日期已从2024年11月12日变更为2025年7月11日。大多数报告者必须在2026年1月22日之前完成所有报告。那些仅就进口含有PFAS的物品的小企业则有时间直到2026年7月11日提交报告。
对受监管实体的影响
TSCA条例下有关PFAS的战略举措对制造商和进口商有很大影响。受监管实体不仅需要考虑其自身操作是否涉及含有PFAS的产品,还必须考虑其供应链中的产品是否可能含有PFAS。报告期的延迟开始使相关实体能够更好地准备这一强制性报告义务。
需要注意的是,尽管因预算和资源问题导致数据收集要求的延迟,进行如此大规模的数据收集和编写强制性报告的窗口时间正在迅速关闭。这显示了EPA坚定的决心,即按照最初提议推进这一报告。
订阅我们的法规更新
随时退订。阅读我们的隐私政策。